How to Check Transmission Fluid in a Manual Transmission
Manual transmissions require checking fluid levels through specific plugs, not dipsticks․ Warm the engine, park on level ground, and locate the fill or drain plug․ Use the correct fluid type specified in your owner’s manual to avoid damage․ Always ensure the vehicle is secure and consult a professional if unsure․
Start by warming up the engine to ensure accurate fluid level reading․ Locate the transmission fluid plug, typically found at the bottom or side․ Remove the plug and check the fluid level, ensuring it reaches the recommended mark․ If low, refill with the appropriate fluid type․ Never overfill, as this can damage the transmission․ If unsure, consult the owner’s manual or a mechanic for guidance․
Inspect the fluid color and consistency․ Clean, healthy fluid should appear bright red or slightly darkened․ If it’s brown, black, or has particles, it may indicate contamination or wear; In such cases, fluid replacement is necessary․ Always use the recommended fluid type to maintain optimal transmission performance and longevity․
For manual transmissions, checking fluid levels regularly can prevent costly repairs․ Ensure the vehicle is on level ground and in neutral or park gear․ Locate the fill plug, remove it, and check the level․ If needed, refill with the specified fluid type․ Avoid using the wrong fluid, as it can damage seals and gears․ Always refer to the owner’s manual for specific instructions․
Checking the transmission fluid in a manual transmission is a crucial maintenance task to ensure smooth gear operation and prevent damage․ Unlike automatic transmissions, manual transmissions typically lack a dipstick, requiring access through specific plugs․ To accurately assess the fluid level, the vehicle must be warmed up and parked on level ground․ The process involves locating the fill or drain plug, removing it, and verifying the fluid level against the recommended mark․ It’s essential to use the correct fluid type specified in the owner’s manual to avoid compromising the transmission’s performance․ Regular checks help identify issues early, such as low fluid levels or contamination, which can lead to costly repairs if neglected․ By following proper steps, you can maintain your manual transmission’s health and ensure optimal functionality․

Preparation and Safety Tips
Always warm up the engine, park on level ground, and engage the handbrake before checking transmission fluid․ Wear protective gear and consult the owner’s manual for specific instructions․
Warm Up the Engine
Start the engine and let it run for a few minutes to warm up the transmission fluid․ This ensures the fluid circulates properly, providing an accurate level reading․ Driving the vehicle for a short distance can also help achieve optimal operating temperature․ A warm engine ensures the fluid is evenly distributed, allowing you to check the level accurately․ If the fluid is too cold, the reading may be misleading, leading to incorrect assessments․ Always avoid checking the fluid when the engine is cold, as this can result in improper level estimation․ Proper warming up is essential for reliable results․
Park on Level Ground
Park your vehicle on a level surface to ensure accurate transmission fluid measurement․ Engage the handbrake securely for safety; Locate the transmission fluid plug, typically at the bottom or side․ Remove it using a wrench or socket, being cautious of any fluid spillage․ Check the fluid level by observing its visibility at the plug opening․ The fluid should be just below the opening when at the correct level․ If low, refill with the appropriate fluid type as specified in your owner’s manual․ Avoid overfilling, as this can damage the transmission․ Always refer to your manual or consult a mechanic if uncertain․
Engage the Handbrake
Engaging the handbrake is a critical step for safety when checking transmission fluid in a manual transmission․ This ensures the vehicle remains stationary and prevents any accidental movement during the process․ Locate the handbrake, typically found between the front seats or under the dashboard, and pull it up firmly to secure the vehicle․ Double-check that the handbrake is fully engaged to prevent the car from rolling․ This step is essential to protect yourself and others from potential hazards while working under the vehicle or accessing the transmission․ Always ensure the vehicle is stable and secure before proceeding with any maintenance tasks․ If unsure about the handbrake’s location or operation, consult your owner’s manual for guidance․
Safety Precautions
Observing safety precautions is essential when checking transmission fluid in a manual transmission․ Always wear protective gear such as gloves and safety glasses to prevent injury from potential spills or debris․ Ensure the vehicle is on level ground and the handbrake is fully engaged to prevent movement․ Never work under a vehicle that is only supported by a jack; use jack stands for added stability․ Keep children and pets away from the work area to avoid distractions or accidents․ If the vehicle is equipped with an automatic emergency brake system, ensure it is activated․ Be cautious of hot components, as the engine and transmission may be warm after driving․ If you are unsure about any step, consider consulting a professional mechanic to avoid risks․ Proper safety measures ensure a smooth and incident-free maintenance process․
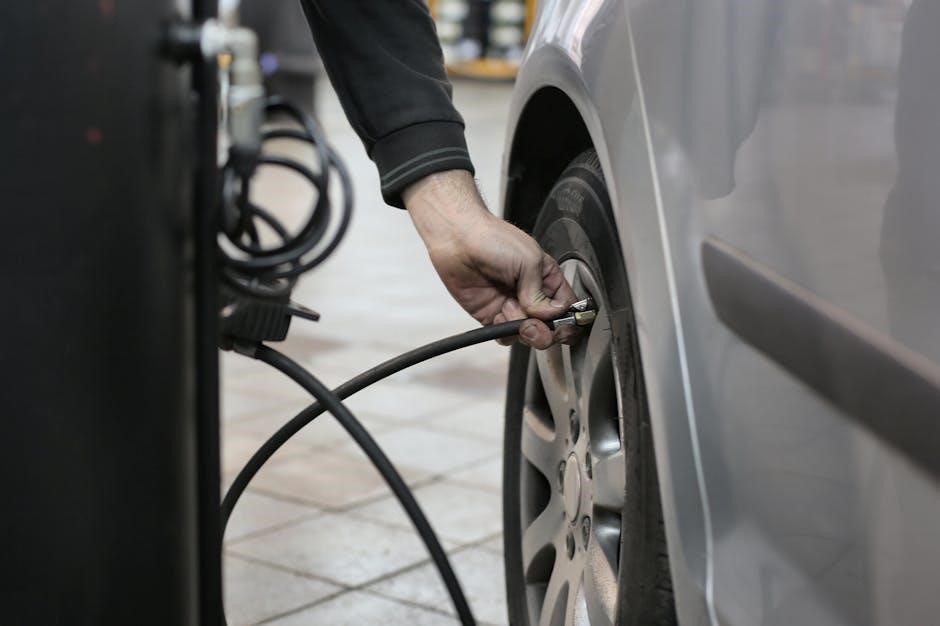

Locating the Transmission Fluid
Manual transmissions typically lack a dipstick, so the fluid level is checked via filler or drain plugs․ These plugs are usually located at the bottom or side of the transmission․ Always consult your owner’s manual for precise locations and instructions to avoid confusion or damage during the process․
Understanding Manual Transmission Fluid Access
Accessing transmission fluid in a manual transmission differs from automatics, as there’s no dipstick․ Instead, fluid levels are checked via filler and drain plugs․ These plugs are typically located on the bottom or side of the transmission․ The filler plug is used to add fluid, while the drain plug is for draining old fluid during servicing; Always refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual to find the exact location, as it varies by make and model․ Ensure the car is on level ground and warmed up for an accurate reading․ Proper access ensures safe and effective fluid level checks, preventing potential damage to the transmission system․ Regular checks help maintain optimal performance and longevity․
No Dipstick in Manual Transmissions
Manual transmissions do not have a dipstick for checking fluid levels, unlike automatic transmissions․ Instead, they typically feature one or two plugs located on the bottom or side of the transmission․ These plugs are used to fill or drain the fluid․ The absence of a dipstick means you must remove the filler plug to check the fluid level․ Always consult your owner’s manual to locate these plugs, as their position varies by vehicle make and model․ When checking, ensure the car is on level ground and the engine is warm for an accurate reading․ Using the correct fluid type is crucial, as specified in the manual, to avoid damaging the transmission․ If unsure, a mechanic can assist for precise results․

Locating the Transmission Fluid Plug
Locating the transmission fluid plug on a manual transmission requires careful inspection․ Typically found on the bottom or side of the transmission, it may be positioned near the front or rear of the unit․ Refer to your owner’s manual for specific guidance, as the location varies by make and model․ Some vehicles may have a single plug for both filling and draining, while others have separate plugs for each function․ Ensure the vehicle is parked on level ground to avoid fluid level inaccuracies․ Use a wrench or socket to remove the plug, taking care not to strip the threads․ Always verify the plug’s location before attempting removal to prevent damage or fluid leakage․ If unsure, consulting a mechanic is advisable to ensure proper access and safety․
Checking the Transmission Fluid Level
Check the fluid level by removing the plug and ensuring the fluid reaches the recommended mark․ Use a wrench to remove the plug safely․
Removing the Plug
To remove the transmission fluid plug, ensure the vehicle is securely positioned on level ground․ Use a socket wrench or Allen wrench to unscrew the plug, typically located at the bottom or side of the transmission․ Be prepared for some fluid to drain out as the plug is removed․ Place a drain pan underneath to catch any spillage․ If the plug is stubborn, apply gentle force but avoid stripping the threads․ Once removed, inspect the plug for debris or metal shavings, which could indicate internal wear․ Allow the fluid to drain slightly to check the level accurately․ Ensure the area around the plug is clean to prevent contamination when reinserting it․ Always refer to the owner’s manual for specific instructions on locating and removing the plug correctly․
Checking the Fluid Level
After removing the plug, inspect the fluid level․ Ensure the car is on level ground and the transmission is warm for an accurate reading․ The fluid should be just below the plug hole․ If low, add the specified fluid type slowly, checking frequently to avoid overfilling․ Inspect the fluid for color and consistency—healthy fluid is bright red or slightly darkened․ If it’s brown or black, consider draining and refilling with fresh fluid․ Always consult the owner’s manual for specific instructions and fluid specifications to maintain optimal transmission performance and longevity․
Fluid Level Indicators
For manual transmissions, fluid level indicators are not as straightforward as in automatics․ Typically, the fluid level should be just below the fill plug hole when the transmission is warm and the vehicle is on level ground․ Use the plug’s opening as a visual guide—fluid should barely trickle out when the level is correct․ If the fluid flows freely, it may be overfilled․ Check the owner’s manual for specific markings or guidelines, as some transmissions may have a dipstick or other indicators․ Always ensure the fluid is clean and free from debris․ If unsure, consult a mechanic to avoid overfilling or underfilling, which can damage the transmission․

Evaluating the Transmission Fluid Condition
Inspect the fluid’s color and consistency․ Healthy fluid is bright red or slightly darkened․ If it’s brown, black, or has particles, contamination or wear is indicated․ A burnt smell signals overheating or degraded fluid․ Always compare the fluid’s condition to the owner’s manual guidelines for accuracy․ If unsure, consult a mechanic․
Fluid Color and Consistency
Healthy transmission fluid is typically bright red or amber in color․ If it appears dark brown, black, or milky, it may indicate contamination or degradation․ Check for consistency—smooth, thin fluid is normal, while thick or lumpy fluid suggests contamination․ If the fluid smells burnt or has visible particles, it may be compromised․ Always compare the fluid’s appearance to the color chart in the owner’s manual for accuracy․ If the fluid is discolored or has an unusual texture, it’s a sign that the fluid needs to be changed․ Regular inspection helps prevent damage to the transmission by ensuring the fluid remains in good condition․ Use a clean, white cloth to wipe and inspect the fluid for clarity and impurities․
Signs of Contaminated Fluid
Contaminated transmission fluid can show visible signs such as dark brown or black color, a milky appearance, or tiny particles suspended in the fluid․ A burnt smell indicates overheated fluid, while a gritty texture suggests internal wear․ If the fluid is cloudy or separated, it may have mixed with water or coolant․ These signs indicate the fluid has degraded and needs replacement․ Contaminated fluid can damage transmission components, so it’s crucial to address these issues promptly․ Always use a clean cloth to inspect the fluid and compare its condition to the manufacturer’s guidelines for color and clarity․ If in doubt, consult a professional mechanic to ensure proper maintenance and prevent further damage․

Refilling or Topping Up Fluid
Use the correct fluid type specified in your manual․ Pour slowly with a funnel, avoiding overfilling․ Stop when fluid reaches the recommended level, then replace the plug securely․
Using the Correct Fluid Type
Always use the fluid type recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer, as specified in the owner’s manual․ Manual transmissions require specific lubricants to maintain proper gear function and prevent wear․ Using the wrong fluid can lead to poor performance, increased wear, or even transmission failure․ Common fluid types include gear oil or synthetic transmission fluids, depending on the vehicle make and model․ Ensure the fluid meets the API or SAE standards for manual transmissions․ Never mix different fluid types, as this can degrade the fluid’s performance and damage components․ Refer to your owner’s manual for the exact fluid specification to ensure compatibility and longevity of your manual transmission․
Refilling the Transmission Fluid
Once the fluid level is checked and found to be low, refilling is necessary․ Ensure the vehicle is on level ground and in neutral or park gear․ Locate the transmission fill plug, typically on the side or top․ Use a funnel to pour in the correct fluid type, as specified in the owner’s manual․ Pour slowly to avoid overfilling, checking the level periodically․ Replace the fill plug securely once the fluid reaches the recommended level․ Start the engine and allow it to run for a few minutes to circulate the new fluid․ Turn off the engine and recheck the level to ensure it remains stable․ Overfilling can damage the transmission, so precision is crucial during this process․

Important Considerations
Always consult the owner’s manual for specific instructions, as manual transmissions vary․ Ensure the vehicle is secure and on level ground during checks․ Never overfill, as it can damage the transmission․ Use the correct fluid type to maintain performance and longevity․ If unsure, seek professional assistance to avoid potential damage․ Regular checks help prevent costly repairs and ensure smooth operation․ Always follow safety guidelines to avoid accidents․ Keep track of fluid levels and condition to maintain optimal transmission health․ Address any signs of low or contaminated fluid promptly․ Proper maintenance ensures extended transmission lifespan and reliability․ Stay informed and proactive to prevent issues․ Consulting a mechanic is advisable for complex or unclear procedures․ Prioritize safety and precision when handling transmission fluid․ Regular servicing contributes to overall vehicle performance and longevity․ Be cautious of contaminated or degraded fluid, as it can lead to mechanical failure․ Always use the recommended tools and fluids for accurate results․ Maintain a record of fluid checks and changes for future reference․ Address any unusual symptoms promptly to prevent further damage․ Proper fluid level and condition are critical for smooth gear operation․ Avoid DIY repairs if unsure, as improper techniques can cause irreversible damage․ Ensure all plugs are securely tightened after checks or refills․ Keep the transmission area clean to prevent debris contamination․ Be aware of the signs of low fluid, such as slipping gears or unusual noises․ Regular fluid checks are essential for maintaining transmission health․ Address any discrepancies in fluid level or condition immediately․ Proper fluid maintenance is vital for ensuring smooth and efficient transmission performance․ Always prioritize professional advice for complex transmission issues․ Stay vigilant about fluid levels and condition to prevent unexpected breakdowns․ Regular maintenance is key to extending the life of your manual transmission․ Be cautious of incorrect fluid types, as they can damage seals and gears․ Always refer to the owner’s manual for fluid specifications․ Keep the transmission fluid clean and free from contaminants for optimal performance․ Address any fluid-related issues promptly to avoid costly repairs․ Proper fluid management ensures reliable and smooth transmission operation․ Regular checks and maintenance are crucial for preventing transmission failure․ Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for fluid type and level․ Ensure the vehicle is properly supported when working underneath it․ Be aware of the signs of transmission trouble, such as hesitation or grinding gears․ Regular fluid checks help identify potential issues early․ Always use the correct tools and techniques when handling transmission fluid․ Maintain a clean and safe working environment when performing checks or refills․ Address any fluid leaks promptly to prevent further damage․ Proper fluid level and condition are essential for maintaining transmission health․ Always consult the owner’s manual for specific instructions and recommendations․ Regular fluid maintenance is vital for ensuring the longevity and performance of your manual transmission․
Consulting the Owner’s Manual
Consulting the owner’s manual is essential for accurate transmission fluid checks in a manual transmission․ The manual provides specific instructions tailored to your vehicle, including fluid type, location of plugs, and recommended levels․ It often includes diagrams or charts to help locate the transmission fluid plugs, which are typically found on the bottom or side․ The manual may also outline the proper procedure for warming up the engine and ensuring the vehicle is on level ground․ Some manuals emphasize the absence of a dipstick in manual transmissions, directing you to the fill and drain plugs instead․ Always refer to the manual for guidance on fluid color and consistency, as well as signs of contamination․ This ensures you follow the manufacturer’s recommendations precisely, avoiding potential damage from incorrect procedures or fluid types․ Regularly reviewing the manual helps you stay informed about maintenance schedules and troubleshooting tips, ensuring optimal transmission performance and longevity․ By following the manual’s instructions, you can perform fluid checks confidently and effectively, maintaining your vehicle’s health․ Proper consultation of the manual is a cornerstone of DIY transmission maintenance, providing clarity and reassurance for even the most inexperienced owners․
Unlike automatic transmissions, manual transmissions typically do not have a dipstick for checking fluid levels․ Instead, they feature fill and drain plugs located on the bottom or side of the transmission․ These plugs are the primary access points for servicing the fluid․ The absence of a dipstick means you must remove the fill plug to check the fluid level․ Be sure to warm the engine first, as this ensures the fluid is at operating temperature for an accurate reading․ Always refer to your owner’s manual for the correct procedure, as the location and method may vary by vehicle․ Manual transmissions rely on these plugs for fluid maintenance, so understanding their use is crucial for proper care․ This design difference emphasizes the importance of consulting your manual to avoid confusion or errors during fluid checks․
Signs of Low Transmission Fluid
Low transmission fluid levels can cause noticeable issues with your vehicle’s performance․ Common signs include delayed or hesitant gear engagement, unusual grinding or whining noises, and difficulty shifting gears․ You may also experience slipping gears or a lack of response when accelerating․ If the fluid level is critically low, the transmission may overheat, leading to further damage․ Additionally, a check engine light may illuminate if sensors detect abnormal transmission operation․ If you notice any of these symptoms, it is essential to check the fluid level promptly and refill if necessary․ Ignoring these signs can lead to costly repairs, such as damaged gears or clutch packs․ Always address low transmission fluid issues early to maintain your vehicle’s health and performance․

